Cell-SELEX
Cell-based SELEX is a powerful approach for identifying aptamers that can be selectively bind to specific cell-surface proteins, transmembrane receptors or a particular target cell population. Those cells could be bacterial strains or mammalian cells.
Cell-SELEX methodology relies on the differences between the target cells population (positive cells that express the target of interest) and the control cell population (negative cells or counter-selection cells that do not express the target protein). Therefore, the selection procedure generally includes positive selection against the target cells and counter selection against non-target cells to remove nonspecific binding.
Cell-SELEX Advantages
-
- High Specificity and Affinity: Aptamers selected through Cell-SELEX can bind to their targets with high specificity and affinity.
- Versatility: This method can be used to target a wide range of cells, including cancer cells, bacteria, and viruses.
- No Need for Prior Knowledge: Unlike traditional methods, Cell-SELEX does not require prior knowledge of the target’s molecular structure.
Cell-SELEX Applications
-
- Diagnostics: Aptamers can be used as molecular probes to detect disease biomarkers.
- Therapeutics: Aptamers can be developed into therapeutic agents that specifically target diseased cells.
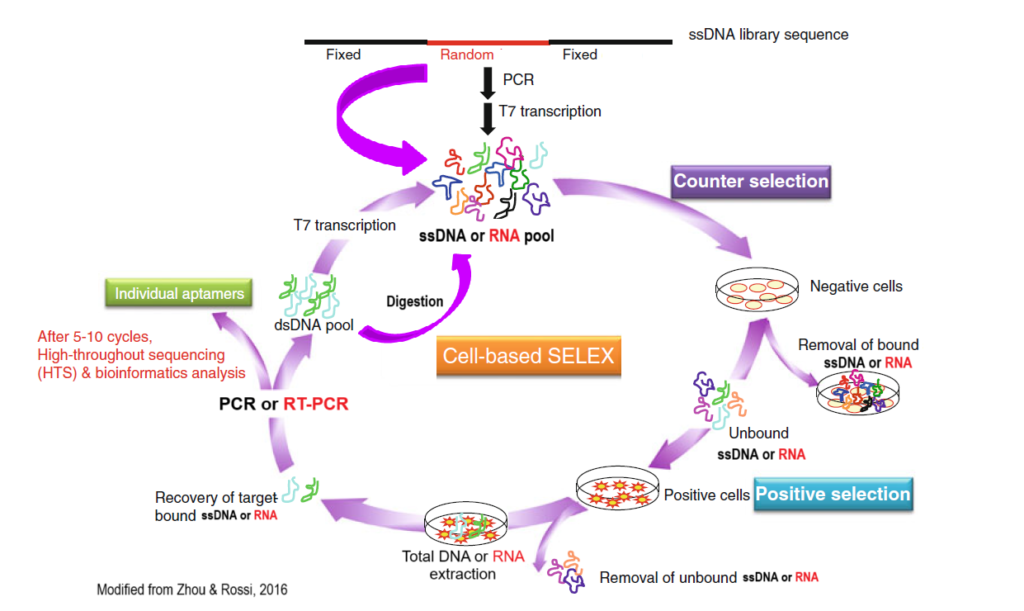
Cell-SELEX Main Steps
-
- Counter selection by incubating library with negative cells that do not express the target proteins;
- Positive selection by incubating recovered unbound sequences with positive cells expressing the target protein.
- Recovery of target-bound sequences
- Re-amplification of recovered sequences and make new pool for the next selection round.
- After 5-12 selection rounds, individual aptamer candidates are identified by Sanger Sequencing or Deep Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis.
Cell-Internalization SELEX
For delivering secondary reagents, such as aptamer-drug, aptamer-siRNAs and aptamer-nanoparticle conjugates, into the target cells, cell internalized aptamers is best choice through cell-internalization SLEX technologies.
Many ligands of cell surface proteins are efficiently internalized after binding their protein targets on the cell surface. Thus, we could identify aptamers not only bind a particular target protein on the surface of cells, but also subsequently internalized into the cell.
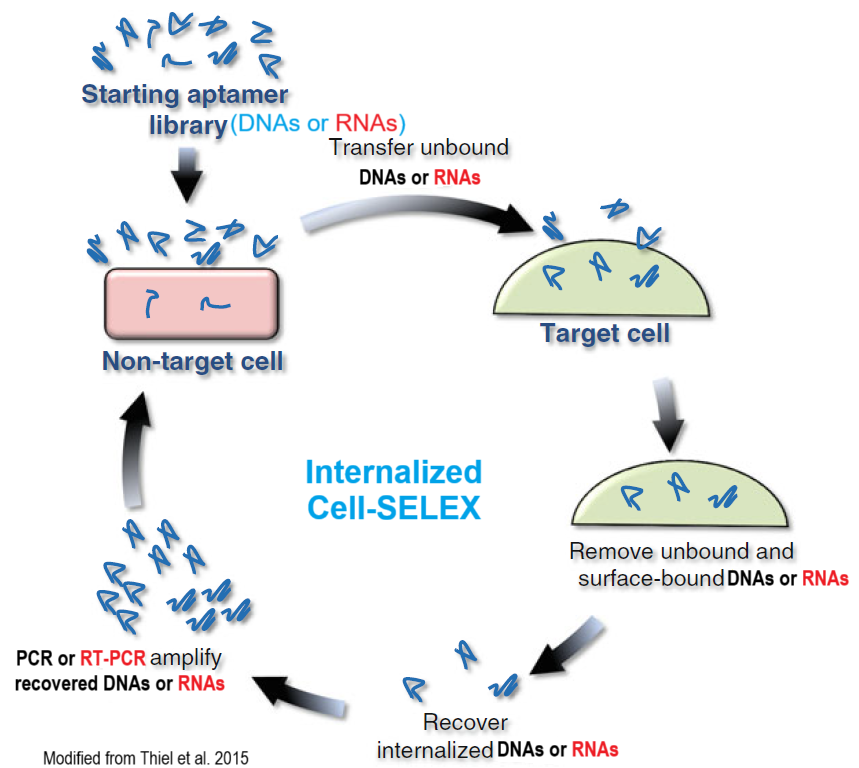
Cell-Internalization SELEX Main Steps
-
- The starting DNA or RNA aptamer library is pre-cleared by incubating the library with non-target cells (The non-target cells are identical to the target receptor-expressing cells, except that they lack the target receptor).
- Those DNAs or RNAs that do not bind or internalize into the non-target cells are then transferred to the target cells. Unbound and surface-bound DNAs or RNAs are discarded and internalized DNAs or RNAs recovered.
- The recovered DNAs or RNAs are amplified using PCR or RT-PCR and the resulting amplified dsDNA digested to ssDNA or in vitro transcribed to RNAs for the subsequent round of selection.
- After 5-12 selection rounds (the selection is terminated when the library reached 90% sequence convergence), individual aptamer candidates are identified by Sanger Sequencing or Deep Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis.
Aptamer Development through Cell-SELEX
Phase I: Library Enrichment via Cell-SELEX
Iterative rounds (5-12 rounds) of screening an initial random library against target cells for positive selection, and negative and/or counter-selection screening against non-target cells.
Criteria: Enrichment 8-30%.
Deliverables: full enrichment progress report
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
Phase II: Sanger Sequencing & Bioinformatic Analysis
Last round of positive binding candidates cloning into sequencing vector for polyclonal preparation, and picking up to 48 clones for Sanger sequencing.
Deliverables: Aptamer candidate sequence information, sequence alignment, family cohort, secondary structure analysis, docking simulation et al..
Timeline: 1-2 weeks
Phase III: NGS Sequencing & Bioinformatic Analysis (optional)
High throughput sequencing (NGS) of last round and representative rounds of positive binding and negative binding, bioimformatic analysis to identify the potential top 5-10 aptamer candidates. Ranked according to the ratio of their representation in the positive round as compared to control population(s).
Deliverables: NGS analysis full report
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
Phase IV: Aptamer Candidate Synthesis, Affinity Determination and Specificity Assessment
Each aptamer candidate (up to 8) is synthesized and quantitatively tested for Kd affinities.
Deliverables: 10 nmol each aptamer candidates, and full assay report showing KD value and specificity for each aptamer candidates.
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
Phase V: Aptamer Optimization & Assay Development
Depends on the criteria set by clients, the cost and timeline will be different.
Deliverables: Full assay development report and 10m nmol optimized aptamers.
Timeline: 2-4 weeks
Packages for your Cell-SELEX project
| Basic Package | Standard Package | Premium Package | Premium plus Package | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I: Library Enrichment via Cell-SELEX | ||||
| Phase II: Sanger Sequencing & Bioinformatic Analysis | ||||
| Phase III: NGS Sequencing & Bioinformatic Analysis | ||||
| Phase IV: Aptamer Candidate Synthesis, Affinity Determination and Specificity Assessment | ||||
| Phase V: Aptamer Optimization & Assay Development | ||||
| Package Cost* | inquiry | inquiry | inquiry | inquiry |
1) Fusion BioLabs guarantees the services;
2) Fusion BioLabs owns its proprietary processes of aptamer development. However, the client owns full rights to the aptamers Fusion BioLabs developed for the client;
3) For multiple targets aptamer development, please contact us for special pricing.
References
1. Thiel WH, et al. (2015) Cell-internalization SELEX: method for identifying cell-internalizing RNA aptamers for delivery siRNAs to target cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1218: 187-199.
2. Zhou J and Rossi J (2016) Evolution of cell-type-specific RNA aptamers via live fell-based SELEX. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1421: 191-214.
