Aptamer-based Biomarker Discovery
Biomarkers are biological molecules that indicate a normal or abnormal process, or a condition or disease. They can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments.
Biomarker discovery is a fascinating and crucial area in medical research. The process of discovering biomarkers involves several steps:
Identification: Researchers identify potential biomarkers by studying biological samples like blood, urine, or tissue.
Validation: These potential biomarkers are then validated through rigorous testing to ensure they are reliable and specific to the condition being studied.
Qualification: Finally, biomarkers are qualified for clinical use, meaning they are proven to be useful in a clinical setting for diagnosing or monitoring a disease.
Modern techniques such as genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics have significantly advanced the field.
Fusion BioLabs develop a powerful and integrated technology, which is termed Aptamer-Based Biomarker Discovery (ABBD). Fusion BioLabs biomarker development technology is an advanced method for identifying biomarkers directly from biological samples, offering potential for early disease detection, personalized medicine, and the development of targeted therapies. It also offers profound insights into diagnosing of various diseases. This innovative strategy involves three crucial steps: traditional differential cell-SELEX, affinity pull-down, and mass spectrometry. Here’s a brief overview of how it works:
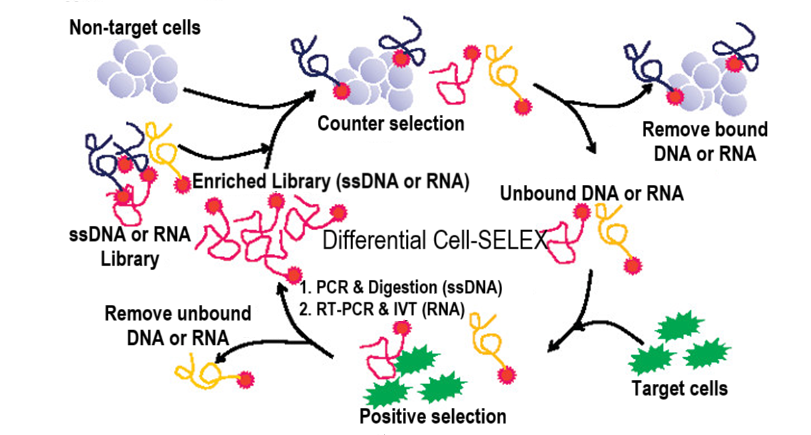
Phase I: Differential Cell-SELEX to Screen Cell-Specific Aptamers
Specific nucleic acid sequences (aptamers) are selected for their ability to bind to target molecules through iterative rounds of selection, amplification, and enrichment.
Criteria: Enrichment 8-30%.
Deliverables: full enrichment progress report
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
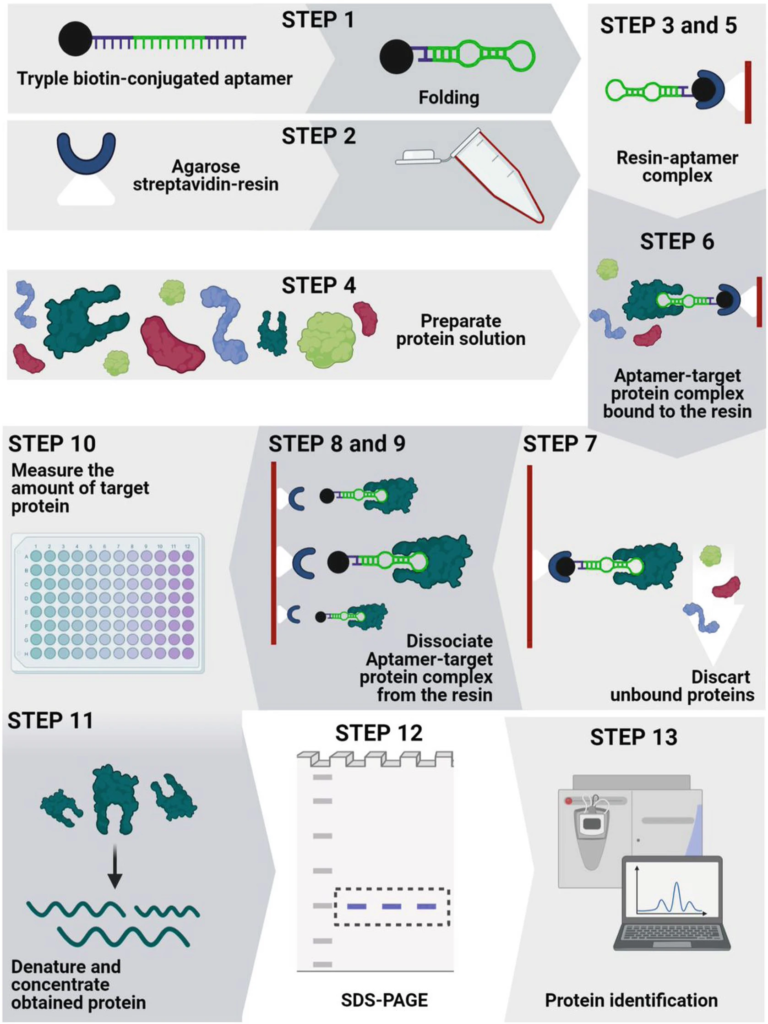
Phase II: Affinity Pull-down to Isolate Biomarker candidates
The selected biotinylated aptamers are used to capture and isolate target biomarkers from complex biological samples.
Deliverables: full aptamer affinity pull-down report
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
Phase III: Biomarker Identification by Mass Spectrometry
The captured biomarkers are identified and quantified using mass spectrometry, providing precise information about their presence and concentration in the sample.
Deliverables: full MS raw data and identification report
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
Affinity Aptamer Pull-down Assay
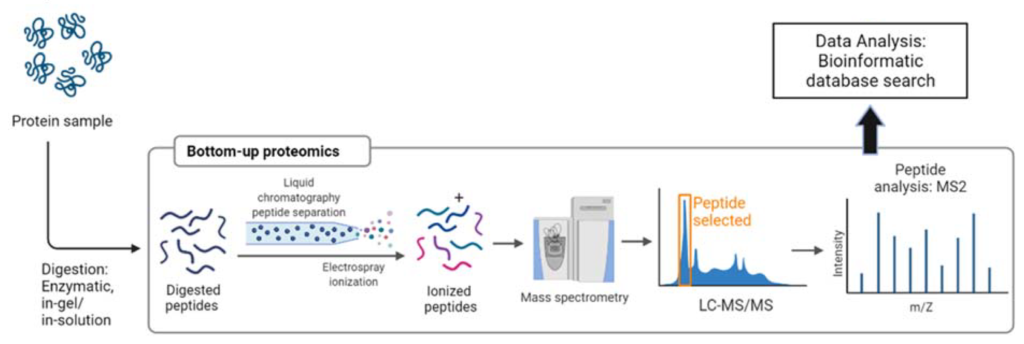
Biomarker Identification by MS
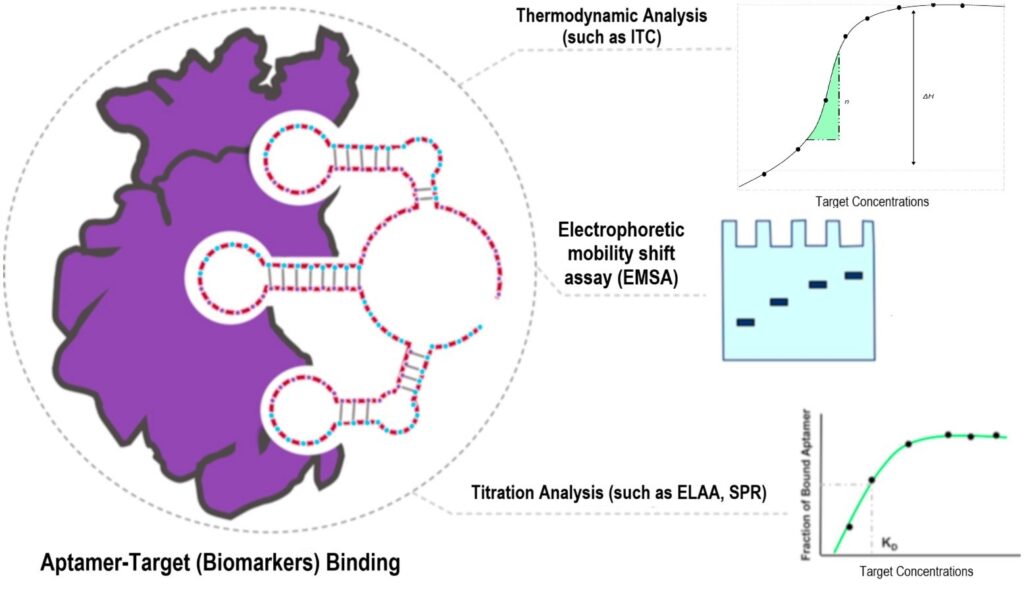
Phase IV: Binding Assay to Validate Biomarker and Aptamer Affinity
The binding of aptamer with the target ligand is validated by surface plasmon resonance, and other affinity binding assay.
Deliverables: full aptamer-biomarker candidate binding and affinity report
Timeline: 2-3 weeks
This strategy allows us to
- Identify aptamers that bind specifically to target cells.
- Identify aptamer-binding biomarkers from target cell membrane
Fusion BioLabs offer the following packages for biomarker identification.
| Basic Package | Standard Package | Premium Package | Premium plus Package | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I: Differential Cell-SELEX to Screen Cell-Specific Aptamers | ||||
| Phase II: Affinity Pull-down to Isolate Biomarker candidates | ||||
| Phase III: Biomarker Identification by Mass Spectrometry | ||||
| Phase IV: Binding Assay to Validate Biomarker and Aptamer Affinity | ||||
| Package Cost* | inquiry | inquiry | inquiry | inquiry |
1) Fusion BioLabs guarantees the services.
2) Fusion BioLabs owns its proprietary processes of biomarker discovery. However, the client owns full rights to the aptamers developed and biomarker identified for the client.
3) For multiple sample biomarker identification, please contact us for special pricing.
References
- Berezovski, MV et al. (2008) Aptamer-Facilitated Biomarker Discovery (AptaBiD). J. AM. CHEM. SOC. 2008, 130, 9137–9143.
- Thevendran, R and Citartan, M (2022) Assays to Estimate the Binding Affinity of Aptamers. Talanta 238 (2022) 122971.
- Ana Paula de Jesus Santos et al. (2022) Selection and application of aptamer affinity for protein purification. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2466: 187-203.